Basic AI Chatbot Pricing: A simple chatbot that can answer questions about a product or service might cost around $10,000 to develop.
Read More
TL; DR

LLM vs NLP serve different purposes – NLP is ideal for structured, task-specific language processing, while LLMs excel in generative AI, conversational interactions, and complex text understanding.

NLP vs LLM: Choosing the right approach depends on business needs – NLP is best for automation, text classification, and sentiment analysis, whereas LLMs are suited for AI-driven content creation, chatbots, and reasoning-based applications.

LLMs require higher computational power than NLP – While NLP models can run efficiently on standard hardware, LLMs need substantial GPU/TPU resources, making them more resource-intensive.

Businesses can combine NLP and LLMs for a hybrid AI strategy – NLP ensures efficiency in structured tasks, while LLMs provide flexibility and adaptability in language generation and customer engagement.

Adopting the right AI model enhances automation and innovation – By leveraging NLP vs LLM effectively, businesses can streamline operations, enhance customer experiences, and improve decision-making.
AI-driven language processing has become a cornerstone of modern business operations, enabling automation, enhancing customer interactions, and improving decision-making. As organizations increasingly integrate AI into their workflows, selecting the right language processing approach remains a critical challenge: NLP vs LLM—Which one aligns best with business needs?
The global Natural Language Processing (NLP) market is projected to reach USD 42.47 billion by 2025, with a CAGR of 38.40% between 2024 and 2034, underscoring the rising demand for AI-driven text analysis and automation
Natural Language Processing (NLP) utilizes linguistic rules, statistical models, and machine learning to analyze and process structured text efficiently. It excels in applications such as sentiment analysis, information retrieval, and text classification.
Large Language Models (LLMs) like GPT-4 and BERT, on the other hand, leverage deep learning to generate human-like text, comprehend complex language patterns, and perform multi-task learning. LLMs are ideal for conversational AI, content generation, and real-time text synthesis.
This blog explores the differences between NLP and LLMs, analyzing their strengths, limitations, and ideal applications. By understanding LLM vs NLP, AI strategists, product managers, and business leaders can make data-driven decisions to optimize their AI-powered language processing strategies.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) is a specialized field of artificial intelligence (AI) that focuses on enabling computers to understand, process, and analyze human language in a structured and meaningful way. Unlike Large Language Models (LLMs), which are designed for a wide range of language-related tasks, NLP is often task-specific and applies a combination of linguistic rules, statistical models, and deep learning techniques to extract insights from text data.
NLP plays a crucial role in various business applications, including customer support automation, text analysis, and real-time data processing, making it an essential tool for organizations looking to enhance their AI-driven communication strategies.
Enhance automation, streamline operations, and improve decision-making with the right AI model.
Get AI IntegrationNLP consists of multiple core components that help machines process human language effectively. Some of the fundamental elements include:
✔ Tokenization: Dividing text into individual words, phrases, or sentences to facilitate analysis.
✔ Part-of-Speech (POS) Tagging: Identifying grammatical categories such as nouns, verbs, adjectives, and more.
✔ Named Entity Recognition (NER): Extracting proper names, locations, dates, and other key information from text.
✔ Sentiment Analysis: Analyzing emotions behind text, helping businesses understand customer feedback.
✔ Dependency Parsing: Examining the grammatical relationships between words to understand sentence structure.
These components allow NLP to interpret textual data accurately, making it highly valuable for a variety of language-based AI applications.
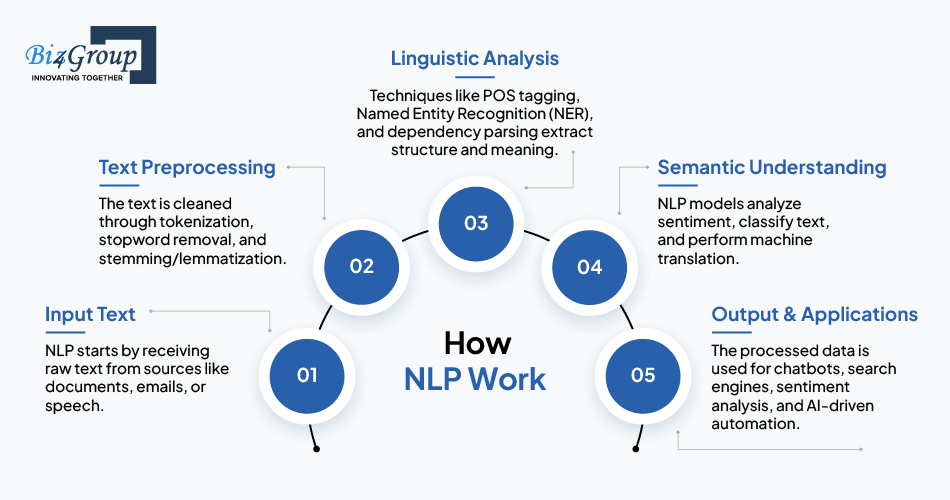
The text is cleaned and structured using:
✔ Tokenization (Splitting text into words/sentences)
✔ Stopword Removal (Filtering out common words like “the,” “is”)
✔ Stemming/Lemmatization (Converting words to their root forms, e.g., “running” → “run”)
The text is analyzed to extract grammatical and contextual meaning using:
✔ Part-of-Speech Tagging (POS) (Identifies nouns, verbs, adjectives, etc.)
✔ Named Entity Recognition (NER) (Detects names, dates, locations)
✔ Dependency Parsing (Understands sentence structure)
NLP models understand the meaning using:
✔ Sentiment Analysis (Detects emotions like positive/negative sentiment)
✔ Text Classification (Categorizes content, e.g., spam detection)
✔ Machine Translation (Converts text into different languages)
The processed text is used for applications like:
✔ Chatbots & Virtual Assistants
✔ Search Engines & AI-powered Recommendations
✔ Automated Text Summarization & Content Analysis
Over time, different techniques have been developed to enhance natural language processing capabilities. The most commonly used methods include:
Each technique has its advantages and limitations, with modern NLP models increasingly relying on neural networks and deep learning architectures to enhance their accuracy and performance.
NLP is widely used across various industries to improve efficiency, automation, and customer interactions. Some of its most common applications include:
✔ Chatbots & Virtual Assistants: AI-powered bots for customer support and FAQ automation (e.g., IVR systems, AI assistants).
✔ Text Summarization: Extracting key insights from lengthy articles and reports (e.g., news aggregation tools).
✔ Spam Detection: Filtering out unwanted emails and messages using machine learning models.
✔Sentiment Analysis: Analyzing customer reviews and social media feedback to understand public perception.
✔ Named Entity Recognition (NER): Extracting important data from legal documents, medical records, and financial reports.
NLP is a foundational AI technology that continues to evolve, enabling businesses to automate processes, enhance decision-making, and optimize communication through advanced language processing.
From sentiment analysis to conversational AI, we develop custom NLP & LLM solutions for your needs.
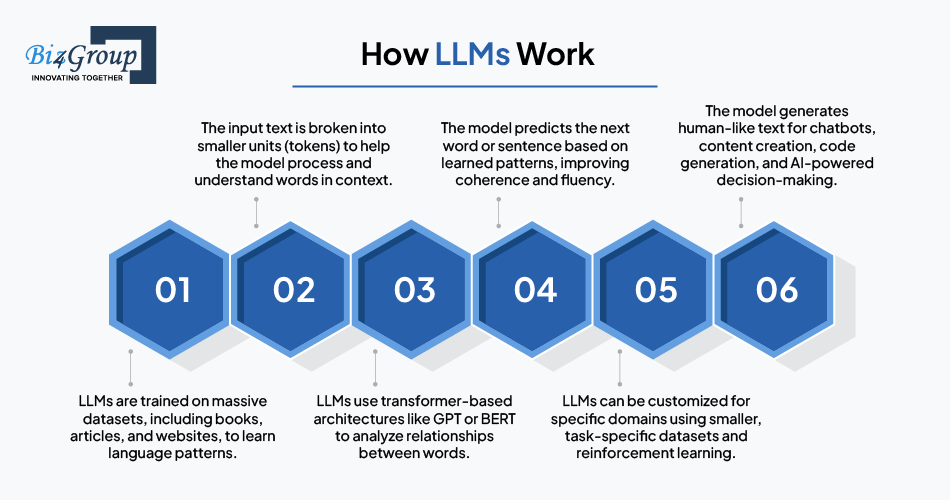
Talk to an AI SpecialistLarge Language Models (LLMs) are deep learning-based AI models designed to understand, generate, and process human language at an advanced level. These models are trained on massive datasets containing diverse text sources, including books, articles, websites, and structured knowledge bases. Unlike traditional Natural Language Processing (NLP) models, which are often task-specific, LLMs have a broad, flexible understanding of language and can perform a wide range of text-based tasks without extensive retraining.
Prominent LLMs like GPT-4, BERT, and PaLM excel at natural language generation (NLG), contextual comprehension, and reasoning-based tasks, making them highly versatile across multiple industries.
✔ Conversational AI (Chatbots, Virtual Assistants)
✔ Content Generation (Blogs, Summaries, Reports)
✔ Code Assistance (AI-powered coding tools)
✔ Machine Translation & Sentiment Analysis
LLMs stand out due to their ability to adapt, learn, and generate human-like text efficiently. Some of their defining features include:
✔ Natural Language Generation (NLG): Produces coherent, fluent, and contextually relevant text, making it ideal for chatbots, automated writing, and AI-driven content creation.
✔ Zero-shot & Few-shot Learning: Can perform tasks with little or no specific training data, allowing businesses to deploy LLMs without extensive fine-tuning.
✔ Contextual Understanding: Analyzes long-form text and understands nuanced queries, making it effective for conversational AI and document summarization.
✔ Scalability: Easily integrates into various applications, from automated customer support to advanced creative writing tools.
These features enable LLMs to handle diverse language-related tasks with greater adaptability than conventional NLP models.
Several LLMs have been developed by leading AI research companies, each specializing in different language-related tasks:
Each of these LLMs has unique strengths, and businesses can leverage them based on specific use cases.
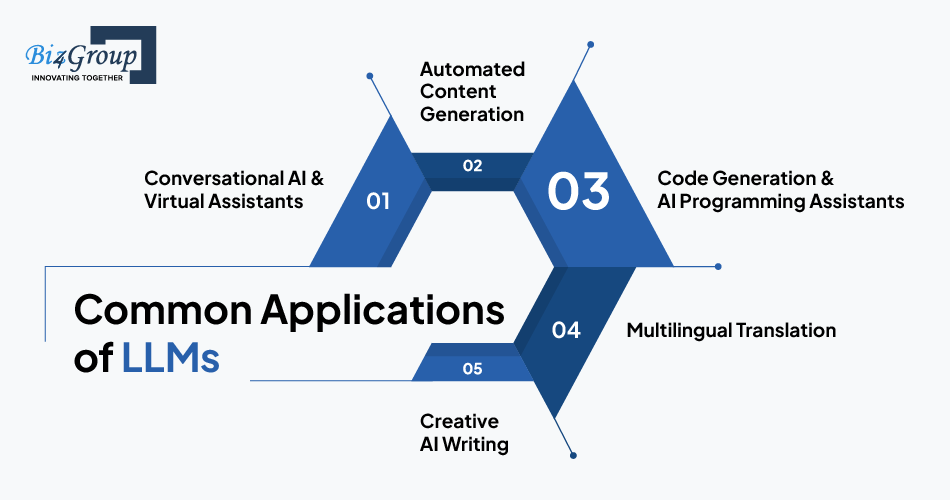
LLMs have transformed industries by enabling intelligent automation and high-quality content generation. Some of their most impactful business applications include:
✔ Conversational AI & Virtual Assistants: Advanced AI chatbots and voice assistants capable of engaging in natural conversations and handling complex queries.
✔ Automated Content Generation: AI-driven blog writing, ad copy creation, and marketing content for businesses looking to scale content production.
✔ Code Generation & AI Programming Assistants: LLM-powered tools like GitHub Copilot assist developers by suggesting code snippets, debugging errors, and automating repetitive coding tasks.
✔ Multilingual Translation: Real-time language translation for businesses operating across multiple countries, enabling seamless communication.
✔ Creative AI Writing: LLMs can generate stories, screenplays, poetry, and even personalized email drafts, making them valuable for creative industries.
With their ability to understand, generate, and process text in a human-like manner, LLMs have become an essential tool for businesses looking to enhance automation, efficiency, and AI-driven decision-making.
The following table provides a detailed comparison of NLP (Natural Language Processing) vs LLM (Large Language Models) across key factors:
|
Factor |
NLP (Natural Language Processing) |
LLM (Large Language Model) |
|
Scope |
Designed for task-specific language processing (e.g., sentiment analysis, text classification, machine translation). |
Versatile and capable of handling multiple text-based tasks, including content creation, reasoning, and contextual understanding. |
|
Training Data |
Requires smaller, domain-specific datasets, often labeled and structured for a particular use case. |
Trained on massive, diverse datasets from various sources (books, articles, websites) to develop broad linguistic understanding. |
|
Computational Needs |
Low to moderate; can run efficiently on regular CPUs and moderate hardware. |
High; requires significant computing power, often leveraging GPUs or TPUs for model training and inference. |
|
Performance |
High accuracy in structured tasks with predefined rules and clear linguistic structures. |
Excels in contextual reasoning and generative tasks, but may sometimes produce inaccurate or biased results. |
|
Interpretability |
Transparent and explainable due to rule-based and deterministic nature. |
Often considered a "black box", making it difficult to trace or interpret how decisions are made. |
|
Customization & Fine-Tuning |
Requires manual feature engineering or retraining for new tasks. |
Can be fine-tuned for specific domains, though it requires large datasets and computational resources. |
|
Real-time Processing |
Fast and efficient, ideal for low-latency applications such as spam detection and chat bots. |
Slower response time, especially for complex queries, due to the need for deep contextual understanding. |
|
Language Generation |
Limited to predefined responses and structured outputs. |
Capable of generating human-like, coherent text, making it useful for creative writing, chatbots, and automated reports. |
|
Adaptability & Learning |
Static models that require retraining to improve accuracy or adapt to new domains. |
Dynamic and adaptive, capable of learning from minimal examples using zero-shot, few-shot, or transfer learning. |
|
Bias & Ethical Concerns |
Less prone to bias due to structured training and deterministic logic. |
Can inherit biases from training data, requiring active monitoring and filtering for ethical AI usage. |
|
Scalability |
Easily scalable for specific use cases without extensive retraining. |
Scales well across multiple domains, but requires massive computational resources for scaling. |
|
Cost & Resource Efficiency |
Lower cost for development, training, and deployment. Affordable for businesses with limited AI budgets. |
High cost due to training complexity, model size, and resource requirements. More suited for large-scale enterprises. |
|
Use Cases |
Best suited for sentiment analysis, text classification, named entity recognition (NER), chatbots, and search engines. |
Ideal for conversational AI, generative content, coding assistants, real-time translation, and multimodal applications. |
Natural Language Processing (NLP) is widely used across industries to automate text processing, improve efficiency, and enhance customer interactions. From chatbots to legal document analysis, NLP helps businesses extract valuable insights from textual data while minimizing manual effort. Below are some key use cases of NLP:
|
Use Case |
Description |
Example |
|
Customer Support Automation |
Businesses use NLP-based chatbots and virtual assistants to handle frequently asked questions (FAQs), provide real-time support, and reduce response times. These AI-driven systems can understand customer queries, retrieve relevant information, and offer solutions, improving customer satisfaction and reducing operational costs. |
AI-powered customer service bots in banking and e-commerce. |
|
Regulatory Compliance & Legal AI |
NLP plays a crucial role in extracting key legal terms, clauses, and obligations from contracts, agreements, and compliance documents. It ensures that organizations stay compliant with regulations by automating document review and risk assessment. |
Law firms and financial institutions use NLP to analyze contracts and identify potential risks. |
|
Market Research & Sentiment Analysis |
Companies leverage NLP-powered sentiment analysis to monitor customer feedback from reviews, social media, and surveys. This helps businesses understand customer sentiment, brand perception, and market trends to make data-driven decisions. |
E-commerce platforms analyzing customer reviews to assess product satisfaction. |
|
Text Categorization |
NLP is used for automated text classification, helping businesses sort and categorize large volumes of unstructured text. It can classify emails, support tickets, research papers, and documents based on predefined categories, streamlining workflow automation. |
AI-powered email filtering for spam detection and priority sorting. |
|
Information Retrieval |
Search engines and AI-powered knowledge management systems rely on NLP to filter relevant results from vast amounts of data. NLP helps in understanding user queries, ranking results accurately, and improving search relevance. |
Google Search uses NLP to refine search queries and provide better recommendations. |
By integrating NLP, businesses can enhance efficiency, automate repetitive tasks, and improve decision-making, making it a powerful tool for AI-driven transformation.
Large Language Models (LLMs) are transforming industries by enabling advanced conversational AI, content generation, and intelligent automation. With their ability to generate human-like text and understand complex queries, LLMs are driving innovation across multiple domains. Below are some key use cases:
|
Use Case |
Description |
Example |
|
Conversational AI & Chatbots |
LLMs power intelligent chatbots and virtual assistants capable of understanding, processing, and responding naturally to user queries. Unlike traditional rule-based chatbots, LLM-driven conversational AI can engage in dynamic, contextual conversations and adapt responses based on prior interactions. |
AI-powered customer support chatbots like ChatGPT, Google Bard, and enterprise virtual assistants. |
|
Creative Content Generation |
LLMs excel in automating content creation, from blog writing and scriptwriting to social media captions and ad copy. These models help businesses scale content production, maintain quality, and improve engagement. |
AI-generated marketing copy, personalized emails, and blog articles created using GPT-4 and Jasper AI. |
|
Automated Coding Assistance |
AI-driven coding assistants use LLMs to help developers with code generation, debugging, and auto-completion. These tools reduce development time, improve code quality, and assist with documentation. |
GitHub Copilot and OpenAI Codex assist developers in writing efficient code with AI-powered suggestions. |
|
Multimodal AI Applications |
LLMs are evolving to integrate text, images, and audio processing, making them useful for multimodal AI applications like text-to-image generation, speech-to-text conversion, and AI-powered design tools. |
OpenAI's DALL·E for text-to-image generation and Whisper for speech recognition. |
|
Personalized AI Assistants |
Businesses and individuals use LLM-based virtual assistants to provide tailored recommendations, automate workflows, and enhance productivity. These AI advisors help users manage business insights, financial analysis, and task automation. |
AI-powered financial advisory assistants, Notion AI for content organization, and AI-driven business analytics tools. |
LLMs provide unmatched scalability and versatility, making them an essential tool for businesses looking to automate workflows, generate content, and enhance human-machine interactions.
Extract meaningful insights, automate workflows, and enhance customer engagement with AI-driven tools.
Start Your AI TransformationChoosing between Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Large Language Models (LLMs) depends on your business goals, computational resources, and the complexity of your AI requirements. While both technologies enable AI-powered language processing, they serve different purposes.
If your business requires task-specific, structured text processing, NLP is the right choice. NLP models are ideal for:
Use Cases: Spam filtering, sentiment analysis, named entity recognition (NER), and text classification.
If your business needs AI with broad contextual understanding, language generation, and adaptability, LLMs are the better choice. LLMs are ideal for:
Use Cases: Conversational AI, creative writing, multilingual translation, and automated code generation.
Many businesses combine NLP and LLMs to achieve the best results. For example:
By evaluating your AI business ideas needs, resource constraints, and AI goals, you can implement the most effective AI-powered language processing strategy to enhance efficiency, customer experience, and automation.
While Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Large Language Models (LLMs) offer powerful AI-driven language processing capabilities, they also present several challenges and ethical concerns that businesses must address. From bias in AI responses to high computational costs, understanding these limitations is crucial for responsible AI deployment.
One of the biggest concerns with LLMs and NLP models is the bias inherited from training data. AI models learn from vast datasets, which may contain racial, gender, or ideological biases, leading to unethical or misleading outputs.
🔹 Example: An LLM trained on biased news sources might generate misleading political content.
🔹 Mitigation Strategy: Regular bias audits, dataset filtering, and fine-tuning with diverse data can help reduce bias.
LLMs, especially deep learning-based models, are often considered black boxes, meaning their decision-making process is difficult to interpret. This can be problematic in high-stakes industries like healthcare, finance, and law, where explainability is crucial.
🔹 Example: An AI-powered loan approval system may reject applications without explaining why.
🔹 Mitigation Strategy: Implementing explainable AI (XAI) models and ensuring transparent decision-making processes.
LLMs sometimes generate incorrect or misleading information, a phenomenon known as hallucination. This can be especially problematic in academic research, medical diagnostics, and fact-based industries.
🔹 Example: An AI model might generate fake references or incorrect scientific facts.
🔹 Mitigation Strategy: Cross-check AI-generated content with trusted sources and human validation before deployment.
Training and deploying LLMs require vast computational resources, making them expensive and environmentally unsustainable.
🔹 Example: GPT-4 and similar models require massive GPU/TPU clusters, consuming significant energy.
🔹 Mitigation Strategy: Optimize AI efficiency by using smaller, fine-tuned models and leveraging serverless or edge AI solutions.
AI models process sensitive user data, raising concerns about privacy violations and unauthorized data usage. Compliance with regulations like GDPR, CCPA, and HIPAA is essential for businesses integrating NLP and LLMs.
🔹 Example: AI chatbots storing sensitive customer conversations without consent.
🔹 Mitigation Strategy: Implement data encryption, user consent mechanisms, and federated learning for privacy protection.
LLMs can be misused for deepfake generation, plagiarism, and misinformation spread, raising ethical concerns about their real-world impact.
🔹 Example: AI-generated fake news articles or plagiarized research papers.
🔹 Mitigation Strategy: Establish AI ethics guidelines, content verification tools, and human oversight for AI-generated content.
By addressing these challenges proactively, businesses can build trust, enhance AI reliability, and create responsible AI solutions that align with ethical and regulatory standards.
Optimize your AI investments by choosing the right NLP and LLM strategy for your business.
Schedule a Free ConsultationThe rapid evolution of AI-driven language models continues to reshape industries, enhancing automation, creativity, and decision-making. As NLP and LLMs advance, businesses can expect transformative trends that will further optimize AI’s efficiency, interpretability, and real-world applications. Below are some key trends shaping the future of Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Large Language Models (LLMs):
One of the biggest challenges with LLMs is their high computational cost and energy consumption. Future developments will focus on smaller, optimized LLMs that deliver high performance while consuming fewer resources.
🔹 Example: The emergence of lightweight, domain-specific LLMs that require fewer GPUs but still provide high accuracy.
🔹 Impact: More accessible AI adoption for businesses with limited computational resources.
Rather than choosing NLP vs LLM, businesses are increasingly adopting hybrid AI models that integrate both approaches. These models combine structured language processing with deep learning capabilities for better performance.
🔹 Example: AI chatbots using NLP for predefined queries and LLMs for complex, context-driven conversations.
🔹 Impact: More accurate, cost-effective AI solutions that optimize efficiency and scalability.
As regulatory scrutiny on AI grows, there is a pressing need for transparent and interpretable AI models. Explainable AI (XAI) will play a crucial role in making NLP and LLMs more accountable.
🔹 Example: AI models that can justify their decisions in high-stakes industries like finance, law, and healthcare.
🔹 Impact: Improved trust in AI, reduced bias, and enhanced regulatory compliance.
Many AI applications currently rely on cloud-based LLMs, but future advancements will bring real-time, edge AI models that run on local devices (smartphones, IoT, embedded systems).
🔹 Example: AI-powered voice assistants and document processing tools running without internet dependency.
🔹 Impact: Faster response times, enhanced privacy, and reduced reliance on cloud computing.
The future of AI is not just text-based—it’s multimodal, meaning models will process and generate text, images, audio, and video seamlessly.
🔹 Example: AI-powered video summarization, speech-to-text AI, and text-to-image synthesis (like OpenAI’s DALL·E and Google’s Gemini).
🔹 Impact: Expanded AI capabilities across industries, enabling more interactive and dynamic applications.
As AI becomes more adaptive, LLMs will enable hyper-personalized digital assistants and autonomous decision-making AI agents that can learn user preferences, automate complex workflows, and optimize decision-making.
🔹 Example: AI-powered financial advisors, personalized learning assistants, and self-improving business intelligence tools.
🔹 Impact: More intelligent, self-learning AI systems that provide customized solutions based on user behavior.
Selecting the right AI development partner is crucial for businesses aiming to integrate NLP and LLM-powered solutions effectively. Experienced AI firms specialize in developing custom NLP applications, AI-driven chatbots, conversational AI systems, and LLM-based automation tools that enhance efficiency and drive business growth.
By leveraging advanced AI technologies, these companies help businesses streamline workflows, improve customer engagement, and extract valuable insights from unstructured data. Whether it’s automated content generation, predictive analytics, or real-time language processing, expert AI developers ensure that solutions are scalable, high-performing, and tailored to business needs.
Among the industry leaders, Biz4Group delivers AI-driven innovations that empower organizations to stay ahead in the competitive landscape. From enterprise AI integration to intelligent virtual assistants and data-driven automation, partnering with a trusted AI development company ensures businesses can fully utilize the potential of NLP and LLM technologies for smarter decision-making and improved operational efficiency.
AI is evolving—should you invest in multi-agent systems or stick with a single intelligent model? Our experts help businesses integrate AI the right way for maximum efficiency.
Let’s Build Smart AI TogetherThe decision between NLP vs. LLM depends on your business needs, resource availability, and AI goals. Each offers distinct advantages, making it essential to align your strategy with the right model.
As AI advances, businesses must adapt the right models to drive innovation, improve efficiency, and enhance decision-making. The right AI strategy will unlock new opportunities and streamline operations.
Which AI model suits your business—NLP, LLM, or both? Let us know!
Yes, a hybrid approach is often ideal—NLP can handle structured tasks, while LLMs manage dynamic, conversational, and generative AI applications.
LLMs excel in natural conversations, adapting to open-ended queries, whereas NLP chatbots are more rule-based and structured, making them better suited for FAQs and predefined responses.
Yes, LLMs need significant GPU/TPU resources for processing, whereas NLP models are lightweight and can run efficiently on standard hardware.
NLP is more cost-effective as it requires less computing power and domain-specific data, while LLMs are expensive due to their size, training complexity, and high computational needs.
If your business needs structured data analysis and efficiency, choose NLP. If you require AI-powered content creation, conversational AI, or deep contextual understanding, LLMs are the better choice.
Top AI development companies in the USA specialize in building custom NLP and LLM-powered solutions, helping businesses integrate AI-driven chatbots, automation tools, and data analytics platforms to improve efficiency and decision-making. They provide expert AI consulting, model fine-tuning, and scalable AI implementations tailored to industry-specific needs.
IN YOUR BUSINESS FOR FREE
Our website require some cookies to function properly. Read our privacy policy to know more.